Research Scale Peptide Synthesizers: Demystifying Purity, Synthesis Speed and Waste Generation
Understand what drives peptide synthesis purity, speed, and waste generation
Introduction
Anyone that has performed peptide synthesis, either manual or automated, realizes quickly that each peptide is different. Peptide sequences can vary in length, contain many different amino acids or a few of the same, be soluble or insoluble, contain disulfide bonds, and many more. With any standard synthesis protocol, the “easy” peptide results in both high crude purity and high purified product yield. While a difficult peptide using a standard synthesis protocol delivers crude peptides with low purity that require more downstream work and lower yields of the purified product (or in some situations, no mass identification of the target peptide).
When performing peptide synthesis, it is not uncommon for a peptide containing only 10 amino acids to be considered more “difficult” to synthesize than a much longer 25+ amino acid peptide. Overall success with synthesizing a specific peptide is generally impacted by:
- Peptide Length: the total number of amino acids in the peptide sequence.
- Peptide Sequence: the specific combination and order of the amino acids in the sequence.
- Synthesis Protocol: The set of steps that together add amino acids to the peptide sequence. These include deprotection washes, coupling time, as well as the number of cleaning washes after both deprotection and coupling.
Of these factors, the Synthesis Protocol is the only way one can control the conditions of their syntheses and optimize their protocol to deliver pure peptides in a time-efficient manner.
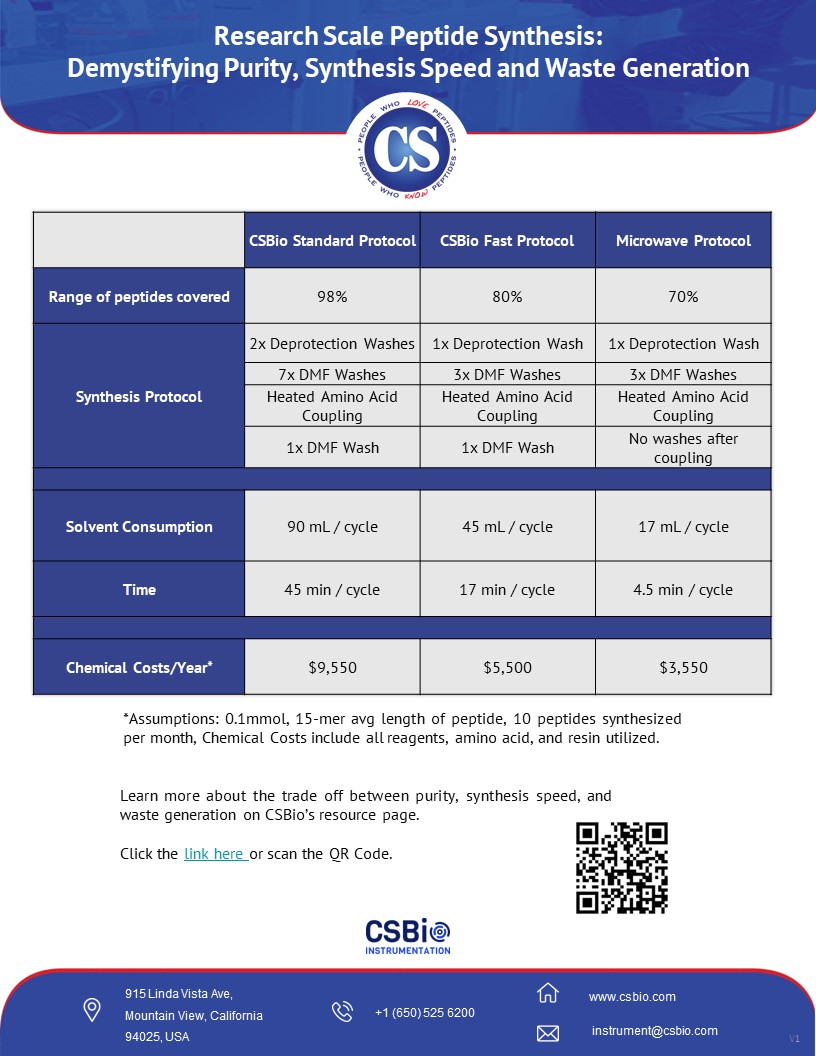
Peptide Synthesis Protocols
When making a peptide, users must balance the purity and yield while also optimizing for synthesis speed and reducing waste for their workflow. Heating the synthesis can allow users to lower the times for deprotection and coupling, leading to faster cycle times. This can be done in a variety of ways including conduction heating and microwave heating. For the best results, heating needs to be delivered uniformly and to consistent temperatures. Conduction heating is scalable from 20 mL up to commercial-size reaction vessels 500L+. It avoids racemization caused by spikes and hotspots typically associated with microwave heating. Conduction heating is also a much more cost-efficient heating method when compared to expensive microwave heating technology.
Synthesis speed and waste also go hand in hand as shown in the chart. It is easy to see that if a protocol contains more DMF washes, 8 vs 3, the protocol with 8 washes will be expected to take longer and generate more waste.
That bodes the question: Why do two instruments aiming to complete the same objective differ so much in their standard protocol?
Higher Purity - The protocol with 8 washes is more likely to deliver a higher purity peptide due to maintaining a cleaner synthesis. The washes after deprotection are essential for ensuring that all the Fmoc group is completely gone before coupling. Doing washes after coupling ensure that your main peak will be your main peak, leaving no room for cross-contamination between amino acid cycles. Look at our case study of the synthesis of a 132-mer peptide on CSBio’s research scale peptide synthesizers
Universally Applicable - A user also benefits from an automated peptide synthesizer that is preloaded with protocols that will work well on nearly all peptides, regardless of sequence or length. The protocol with 8 washes can be run on a wide range of peptide sequences and expect a successful synthesis, not for a fraction of the peptide sequences. Users of the CSBio Peptide synthesizers can easily choose between a conservative or aggressive washing protocol giving them the ability to reduce the number of washings after deprotection and coupling to improve synthesis speed and reduce waste.
Cost to Perform Peptide Synthesis
What’s the raw material cost to run a peptide synthesizer? Well, most research labs will synthesize ~10 peptides a month at the 0.1 mmol scale, usually averaging about 15 amino acids in length. Then it’s largely dependent on the synthesis protocol utilized and the type of raw materials used. Some peptide synthesizer manufacturers require special amino acids and resins to run their synthesis protocol, such as His(Boc) that can be 7 times more expensive than standard His(Trt), or PEG-PS resin that can be twice as expensive as Rink Amide MBHA resin.
When considering the synthesis protocols, the amino acids, resin, and all the reagents and solvents, a typical cost per year will range between $5k to $10k. This considers purchasing the amino acids in 100g bulk (not pre-packaged cartridges), and does not include any disposable or consumable items that the synthesizer manufacturer may require. If you're interested in learning about the details of the cost to perform peptide synthesis and these calculations, just reach out to us.
As users can see, while there may be a marginal potential cost savings from the reduced waste of the microwave protocol, this doesn’t factor in re-running the synthesis in situations that the target peptide is not found. Even without the re-synthesis situation, looking at the total cost per run is negligible when factoring in the much higher purchase price of an expensive microwave synthesizer.
With a CSBio Peptide Synthesizer, users are confident that the provided protocols deliver high-quality results on difficult peptides while allowing users to easily change the protocol to manage synthesis speed and waste. Reach out to us at instrument@csbio.com, schedule a call to learn more, or just ring us directly at +1 650 525 6200 if you’re interested in discussing your peptide synthesizer needs.
About CSBio: For over 30 years, CSBio, a leading peptide and peptide synthesizer manufacturing company located in Silicon Valley, California, has been providing cGMP peptides and automated peptide synthesizers to the global pharmaceutical community. CSBio’s peptide products and peptide synthesizers can be found in production laboratories, universities, and pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
Want to know when new
Resources are released? Be notified
Related Posts
Synthesizing a 132-mer peptide with high purity
Synthesis of peptides at any length requires extreme attention to detail for accuracy and purity of the desired compound...
Research Scale Peptide Synthesizer Comparison - A Guide to Choosing a System that Fits Your Needs
A guide for choosing a research scale peptide synthesizer, comparing the most popular synthesizers on the market today.
About Us
CSBio is a leading peptide and instrumentation manufacturing company located in Silicon Valley, California.
CSBio provides nonGMP and cGMP peptides, peptide APIs, research scale peptide synthesizers, commerical scale peptide synthesizers, DNA/RNA oligonucleotide synthesizers, and preparative HPLC purification equipment.
Useful Links
Instrumentation Contact
915 Linda Vista Ave
Mountain View, CA, 94043
+1-650-525-6200