An Introduction to Process Analytical Technologies in Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS)
A resource on how PATs are implemented in SPPS
What are PATs?
Process Analytical Technologies (PAT) provide information about a chemical synthesis process in real time, monitoring individual steps during a process to provide actionable data. While direct final product purity assessment often occurs post-synthesis, PATs provide in-process information about reactant concentrations and reaction completeness, both crucial factors that impact the quality of the final product. These tools provide invaluable information for Quality Assurance teams in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Monitoring individual steps of a synthesis process improves the efficiency by detecting endpoints to determine when a step is complete, eliminating unnecessary washing steps and reducing reaction times. These changes also reduce cost in the form of waste elimination and labor management, while removing the need for manual sampling improves worker safety.
PATs in SPPS
In solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), there are three commonly used PATs: UV-vis spectroscopy, Refractive Index, and, recently, Raman Spectroscopy.
UV-vis spectroscopy measures the absorbance of a sample over a specified wavelength range. The relationship between absorbance and wavelength is described by the Beer-Lambert law: A = εlc, where A is absorbance, epsilon (ε) is the molar absorptivity, l is the pathlength from the light source and c is the concentration of the solution in units of molarity (mol/L). The molar absorptivity is the measure of how strongly a substance absorbs light at a given wavelength, a value that is specific to that compound and the conditions it is measured under. UV-vis has been utilized to monitor the deprotection and post deprotection wash steps.
Refractive Index (RI) can be used for monitoring deprotection, coupling, and washing during automated SPPS. Refractive index is a unitless measure describing the change in the speed and direction of light in a medium relative to another medium; it is described by the equation n = c/v, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum and v is the speed of light through a given material. The refractive index of a liquid is dependent on the wavelength of light passing through it. For analytical applications the refractive index of a solution is measured at 589.3 nm, a wavelength known as the sodium D-line. The sodium D-line produces a stable, consistent light source, although modern refractometers may utilize other stable monochromatic light sources.
Raman spectroscopy has recently been explored as a PAT for SPPS. Raman spectroscopy takes advantage of inelastic light scattering, in which the energy of the scattered photons is different from that of the incident light source. Raman spectroscopy primarily measures Stokes scattering because it is generally more intense than anti-Stokes scattering at typical operating temperatures. The change in energy from the incident photon to the scattered photon is known as the Raman Shift, with units of inverse wavenumber (cm-1). Raman spectra are plotted as signal intensity versus Raman shift. This unit system allows for direct comparison of vibrational modes independent of the excitation wavelength used. The intensity of the Raman signal is directly proportional to the concentration of a given analyte in a sample, similar to Beer-Lambert behavior, and thus requires calibration with known concentrations for accurate quantitative determination. Raman is used for monitoring all steps in SPPS.
The following chart describes how PATs have been implemented in peptide research and development processes.
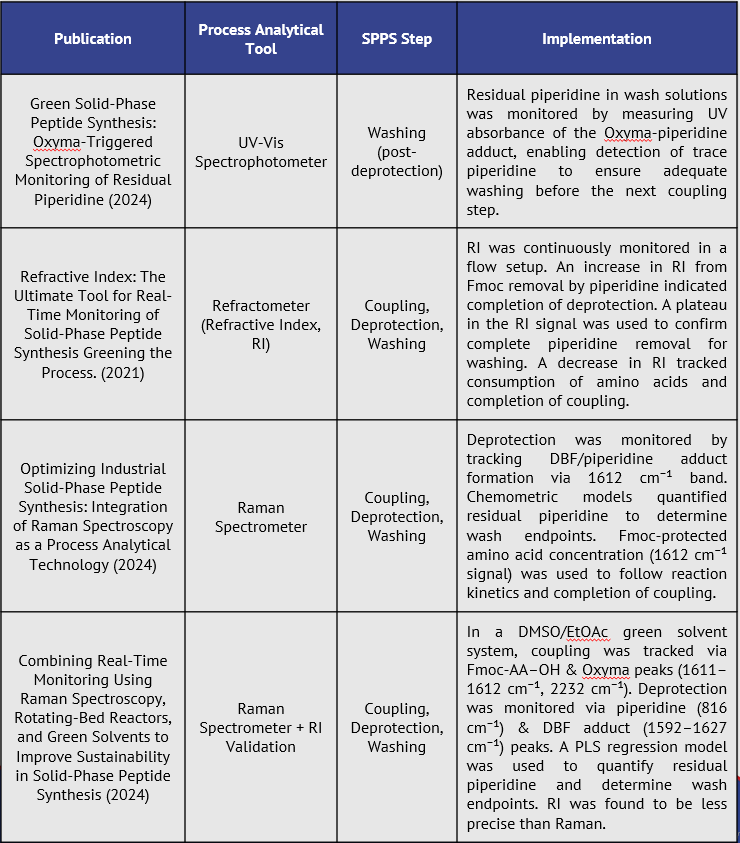
How do PATs compare?
When choosing a PAT, consider the cost, specificity, and how each tool is affected by environmental factors like temperature.
.....
Download the full resource - An Introduction to Process Analytical Technologies in Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) : Download Link
About CSBio: For over 30 years, CSBio, a leading peptide synthesizer manufacturing company located in Silicon Valley, California, has been providing automated peptide synthesizers to the global pharmaceutical community. CSBio’s peptide synthesizers and peptide products can be found in production laboratories, universities, and pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
Want to know when new
Resources are released? Be notified
Related Posts
Synthesizing a 132-mer peptide with high purity
Synthesis of peptides at any length requires extreme attention to detail for accuracy and purity of the desired compound...
Research Scale Peptide Synthesizer Comparison - A Guide to Choosing a System that Fits Your Needs
A guide for choosing a research scale peptide synthesizer, comparing the most popular synthesizers on the market today.
About Us
CSBio is a leading peptide instrumentation manufacturing company located in Silicon Valley, California.
CSBio provides research scale peptide synthesizers, pilot scale peptide synthesizers, commerical scale peptide synthesizers, and DNA/RNA oligonucleotide synthesizers.